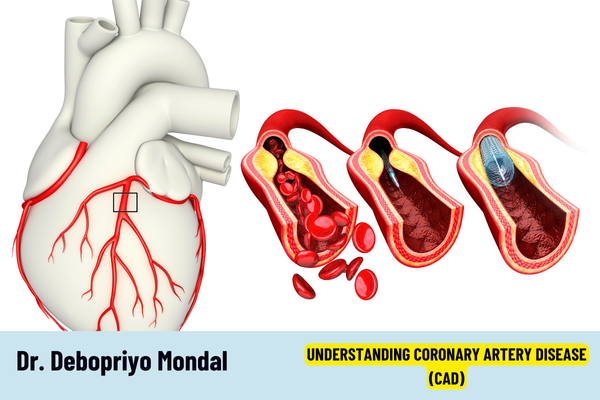
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries due to plaque buildup. These arteries supply blood to the heart muscle, and when they become restricted, the heart’s blood supply is reduced, leading to serious health issues.
The primary cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances form plaque on the artery walls. This buildup can result in reduced blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscle, potentially causing chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or heart attacks.
Several factors increase the risk of developing CAD, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Family history and age are also significant contributors.
Symptoms of CAD may vary, but common signs include chest discomfort, pain in the arms or shoulders, shortness of breath, and fatigue. In some cases, CAD may be asymptomatic until a heart attack occurs.
Preventing CAD involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, such as maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco, and managing stress. Regular medical check-ups can help in early detection and management of the condition.
Understanding coronary artery disease is crucial for taking proactive steps towards heart health. By recognizing the definition and associated risks of CAD, individuals can make informed choices to protect their well-being.